Understanding Hormonal Weight Gain

[Source: carrotsncake.com]
Weight management isn’t always as simple as calories in versus calories out. Your body’s hormones play a crucial role in determining how you gain, maintain, or lose weight. These chemical messengers significantly influence your metabolism, appetite, and fat storage patterns [#1].
What Causes Hormonal Weight Gain?
Hormonal weight gain occurs when your body experiences shifts in its delicate chemical balance. These changes can stem from various factors, including natural aging processes, life transitions like menopause, or underlying medical conditions .
Common triggers for hormonal weight gain include:
- Age-related hormonal changes
- Stress and elevated cortisol levels
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Reproductive hormone fluctuations
- Insulin resistance
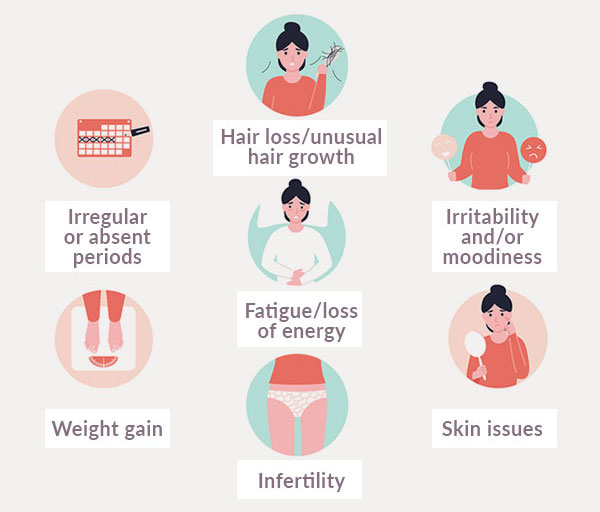
Symptoms and Areas Affected
Hormonal weight gain often manifests differently than weight gain from poor diet or lack of exercise. You might notice:
- Sudden weight changes without lifestyle modifications
- Difficulty losing weight despite healthy habits
- Weight gain in specific areas (especially around the midsection)
- Increased fat storage combined with muscle loss
- Water retention and bloating
Understanding these patterns helps identify whether your weight changes stem from hormonal issues or other factors. This knowledge becomes essential for developing an effective strategy to address the root cause rather than just treating symptoms.
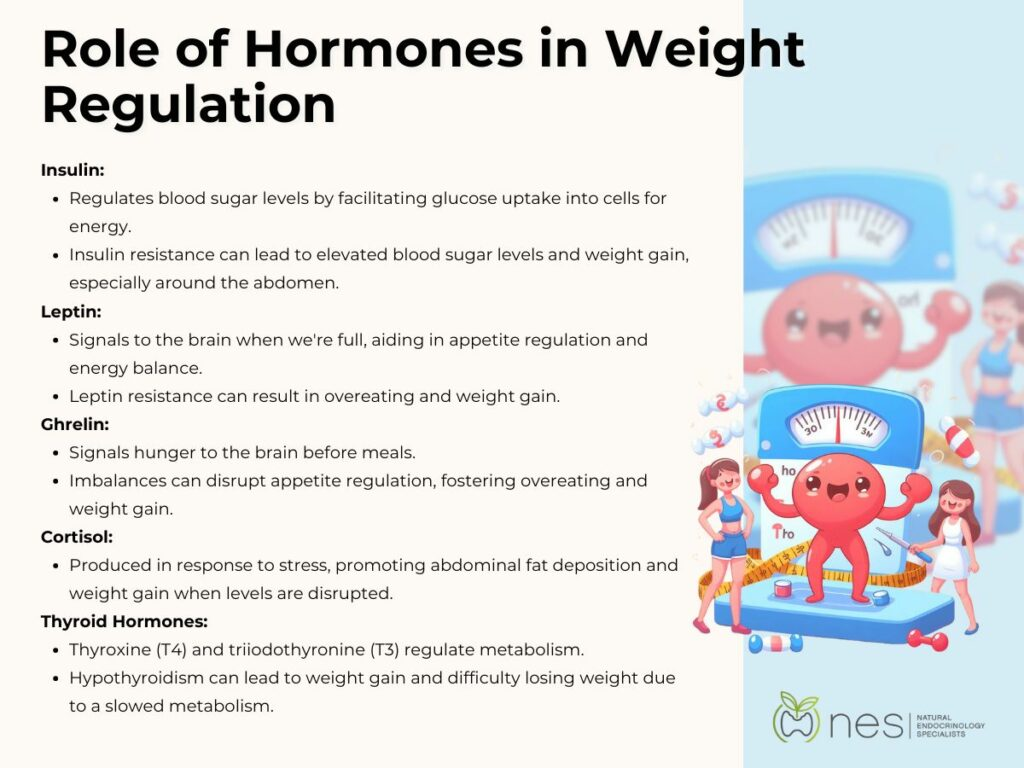
Key Hormones Involved in Weight Gain
[Source: nesaz.com]
Several hormones work together to regulate your body weight, metabolism, and appetite. Understanding these chemical messengers can help you develop better strategies for managing your weight.
Primary Weight-Regulating Hormones
Insulin stands as the body’s primary storage hormone, produced by the pancreas. It helps cells absorb glucose from your bloodstream and can significantly impact fat storage. When insulin levels remain consistently high, your body becomes more prone to storing fat rather than burning it for energy [#2].
Leptin, often called the satiety hormone, signals fullness to your brain. It helps regulate long-term energy balance and body weight. However, many people with obesity develop leptin resistance, where the brain stops responding to these fullness signals .
On the flip side, ghrelin acts as your hunger hormone, increasing appetite and signaling when it’s time to eat. Your ghrelin levels typically rise before meals and fall after eating .
Stress and Metabolic Hormones
Cortisol, produced by the adrenal glands, earned its nickname as the stress hormone. While vital for survival, chronically elevated cortisol levels can lead to increased belly fat storage and intense cravings for high-calorie foods .
Beyond these primary hormones, several others play supporting roles in weight regulation:
- Thyroid hormones: Control your metabolic rate and energy expenditure
- Estrogen: Influences fat distribution and storage patterns
- Growth hormone: Promotes muscle growth and fat breakdown
- Testosterone: Helps build muscle mass and reduce fat storage
By learning simple ways to balance these hormones naturally through lifestyle modifications, you can make your weight management journey more successful. Small changes in diet, exercise, and sleep patterns can create significant improvements in hormonal balance.
Conditions Linked to Hormonal Weight Gain
[Source: womenshealthnetwork.com]
Several medical conditions can disrupt your body’s hormonal balance, making weight management more challenging. Understanding these conditions helps create effective strategies for maintaining a healthy weight.
Common Hormonal Conditions
Hypothyroidism stands out as a significant contributor to unexplained weight gain. When your thyroid gland produces insufficient hormones, your metabolism slows down considerably, leading to weight gain even with normal eating habits. This condition often causes fatigue, cold sensitivity, and difficulty losing weight through traditional methods [#3].
PCOS affects many women of reproductive age, causing hormonal imbalances that make weight control particularly challenging. This condition typically involves insulin resistance, which can trigger increased hunger and fat storage, especially around the midsection. Women with PCOS often notice weight gain despite maintaining their regular eating patterns .
Life-Stage Related Hormonal Changes
Menopause brings significant hormonal shifts that can affect body weight and fat distribution. As estrogen levels decline, many women notice increased belly fat accumulation. This shift in fat storage patterns often occurs even without changes in eating habits or lifestyle.
Sleep disorders, particularly insomnia, can create a cascade of hormonal disruptions. Poor sleep affects cortisol rhythms and hunger hormones, potentially leading to increased appetite and decreased metabolism. Making dietary adjustments, such as limiting certain foods that interfere with sleep, can help manage these effects.
- Endometriosis: Can affect hormone balance and metabolism
- Cushing’s syndrome: Leads to increased cortisol production
- Diabetes: Affects insulin regulation and fat storage
- Premenstrual syndrome: Causes temporary hormonal fluctuations
Managing these conditions often requires a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle modifications. Simple changes like reducing processed carbohydrates and focusing on whole foods can support hormonal balance and weight management goals.
Strategies to Manage Hormonal Weight Gain

[Source: fitpaa.com]
Taking control of hormonal weight gain requires a multi-faceted approach focused on rebalancing your body’s natural systems. While many people focus solely on diet and exercise, addressing the underlying hormonal imbalances proves more effective for long-term success .
Improving Insulin Sensitivity
Balancing blood sugar levels starts with smart food choices. Replace refined carbohydrates with fiber-rich alternatives like quinoa, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens. Adding a 10-minute walk after meals can significantly improve insulin response.
Managing Stress and Cortisol
High stress levels trigger cortisol production, leading to stubborn belly fat. Regular stress management practices make a substantial difference in hormonal balance . Consider these effective techniques:
- Deep breathing exercises – practice for 5 minutes daily
- Regular physical activity, similar to those fat-burning stretches
- Meditation or mindfulness practices
- Setting boundaries in work and personal life
- Engaging in enjoyable hobbies
Balancing Leptin and Ghrelin
These hunger hormones play crucial roles in appetite regulation. Establish consistent meal times and prioritize protein-rich foods at breakfast. Avoid eating close to bedtime to maintain proper hormone cycling.
Supporting Thyroid Function
Optimize thyroid hormone production through dietary choices. Include selenium-rich foods like Brazil nuts and sunflower seeds. Consider having your iodine levels checked, as proper levels support healthy thyroid function.
Maintaining Healthy Estrogen Levels
Balance estrogen naturally by consuming cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower. Regular exercise helps metabolize excess estrogen effectively. Some fitness professionals incorporate specific workout routines that target hormonal balance.
Remember that hormonal balance requires patience and consistency. Small, sustainable changes often yield better results than dramatic lifestyle overhauls. Track your progress with a symptom diary rather than focusing solely on the scale.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Hormonal Balance

[Source: eleatnutrition.com]
Making sustainable lifestyle adjustments plays a vital role in maintaining hormonal equilibrium. Small, consistent changes often create the most significant impact on your body’s hormone regulation.
Avoiding Toxins and Plastics
Environmental factors significantly influence hormone function. Replace plastic food containers with glass or stainless steel options. Choose organic produce when possible, focusing on the dirty dozen list. Consider using natural cleaning products to minimize exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals.
Balancing Blood Sugar
Stable blood sugar levels help regulate multiple hormone systems. A diet rich in whole, plant-based foods prevents excess calorie storage and supports healthy hormone function [#4]. Start your day with alkaline foods to maintain steady energy levels.
Managing Stress Effectively
Chronic stress disrupts hormonal balance and contributes to weight gain. Regular exercise helps manage stress hormones while maintaining lean body mass . Incorporate these stress-reduction techniques:
- Practice mindfulness or meditation daily
- Try gentle yoga sequences
- Use deep breathing exercises
- Take regular breaks during work
- Spend time in nature
Prioritizing Quality Sleep
Poor sleep patterns disrupt hormone production and regulation. Create a consistent bedtime routine and optimize your sleeping environment. Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and free from electronic devices. Consider natural sleep aids like chamomile tea or magnesium supplements if needed.
Limiting Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol interferes with hormone processing in the liver and can increase inflammation. Set clear boundaries around alcohol consumption, such as limiting drinks to special occasions or implementing alcohol-free days. Replace alcoholic beverages with herbal teas or infused water to maintain your lymphatic system health.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Hormonal weight gain presents a complex challenge, but understanding the underlying mechanisms empowers you to take control. The interplay between insulin, leptin, ghrelin, cortisol, and other hormones affects your body weight in multiple ways.
Success in managing hormonal weight gain relies on a multi-faceted approach:
- Regular monitoring of hormone levels through medical check-ups
- Implementing dietary changes that support hormone balance
- Maintaining consistent exercise routines
- Prioritizing stress management and quality sleep
- Reducing exposure to environmental toxins
Final Thoughts
Just as the royal physicians emphasize preventive health measures, addressing hormonal imbalances early can prevent long-term weight management struggles. Small, sustainable changes often yield better results than drastic measures.
Remember that hormonal balance varies among individuals. What works for one person might not work for another. Stay patient with your body as you implement these strategies, and celebrate small victories along the way. Regular consultation with healthcare providers helps fine-tune your approach and maintains progress toward your weight management goals.
By incorporating these science-backed strategies into your daily routine, you can create lasting changes that support both hormonal balance and healthy weight maintenance. Focus on progress rather than perfection, and allow time for your body to respond to these positive changes.